The impact of smoking and alcohol on bone health is a critical area of research that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are lifestyle choices that can have profound effects on various aspects of health, including the skeletal system. Understanding how these substances affect bone density, strength, and overall health is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies for bone-related diseases, such as osteoporosis. This article will explore the mechanisms through which smoking and alcohol influence bone health, the implications for individuals, and potential strategies for mitigating these risks.
Understanding Bone Health
Bone health is a vital component of overall well-being, as bones provide structure, protect organs, anchor muscles, and store calcium. The human skeleton undergoes a continuous process of remodeling, where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue. This process is regulated by a balance between osteoblasts (cells that build bone) and osteoclasts (cells that break down bone). Factors such as age, nutrition, physical activity, and lifestyle choices play significant roles in maintaining this balance.
Bone density, which refers to the amount of bone mineral in a given volume, is a crucial indicator of bone health. Higher bone density typically correlates with stronger bones and a lower risk of fractures. Conversely, low bone density can lead to conditions like osteoporosis, characterized by fragile bones and an increased risk of fractures. Various factors can influence bone density, including hormonal changes, dietary intake of calcium and vitamin D, physical activity levels, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and alcohol consumption.
The Effects of Smoking on Bone Health
Smoking has long been associated with a myriad of health issues, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and various cancers. However, its impact on bone health is often overlooked. Research indicates that smoking can adversely affect bone density and increase the risk of fractures through several mechanisms.
Mechanisms of Bone Damage
- Reduced Blood Flow: Smoking constricts blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the bones. This diminished circulation can impair the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen necessary for bone health.
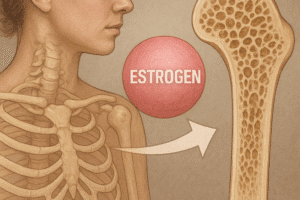
- Hormonal Imbalances: Smoking can disrupt the balance of hormones that regulate bone metabolism, including estrogen and testosterone. In women, smoking is associated with earlier onset of menopause, which can lead to a rapid decline in bone density.
- Increased Osteoclast Activity: Studies have shown that smoking may increase the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. This imbalance can lead to a net loss of bone mass over time.
- Impaired Calcium Absorption: Smoking can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, a critical mineral for bone health. Insufficient calcium levels can contribute to decreased bone density.
Research Findings
Numerous studies have demonstrated a clear link between smoking and decreased bone density. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research found that smokers had significantly lower bone mineral density compared to non-smokers. Additionally, the risk of hip fractures was found to be higher among smokers, particularly in older adults. The cumulative effects of long-term smoking can lead to a substantial increase in fracture risk, making it imperative for individuals to consider the impact of smoking on their bone health.
The Effects of Alcohol on Bone Health
Like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption poses significant risks to bone health. While moderate alcohol intake may have some protective effects on cardiovascular health, heavy drinking is detrimental to bone density and overall skeletal integrity.
Mechanisms of Bone Damage
- Inhibition of Osteoblast Function: Alcohol has been shown to inhibit the activity of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation. This inhibition can lead to decreased bone formation and, consequently, lower bone density.
- Hormonal Disruption: Chronic alcohol consumption can disrupt the balance of hormones involved in bone metabolism, including estrogen and parathyroid hormone. This disruption can lead to increased bone resorption and decreased bone formation.
- Impaired Nutrient Absorption: Alcohol can interfere with the absorption of essential nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, which are crucial for maintaining bone health. Poor nutrition can exacerbate the negative effects of alcohol on bone density.
- Increased Risk of Falls: Alcohol impairs coordination and balance, increasing the risk of falls and subsequent fractures. This risk is particularly concerning for older adults, who may already be at a higher risk for falls due to age-related factors.
Research Findings
Research has consistently shown a correlation between heavy alcohol consumption and decreased bone density. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that individuals who consumed more than two alcoholic drinks per day had significantly lower bone mineral density compared to moderate drinkers or non-drinkers. Furthermore, heavy drinkers were found to have a higher incidence of fractures, particularly in the hip and spine regions.
Combining the Effects of Smoking and Alcohol
The combined effects of smoking and alcohol on bone health can be particularly detrimental. Individuals who engage in both behaviors may experience an exacerbation of the negative impacts on bone density and strength. The synergistic effects of these substances can lead to a higher risk of osteoporosis and fractures compared to individuals who engage in only one of these behaviors.
Strategies for Mitigation
Given the significant impact of smoking and alcohol on bone health, it is crucial to adopt strategies to mitigate these risks. Here are some recommendations:
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve bone health. Various resources, including counseling and nicotine replacement therapies, can support individuals in their efforts to quit.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake to moderate levels can help protect bone health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines moderate drinking as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Nutrition: Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health. A balanced diet rich in these nutrients can help counteract some of the negative effects of smoking and alcohol.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing and resistance exercises can help strengthen bones and improve overall bone density. Physical activity is a crucial component of a healthy lifestyle that supports bone health.
Conclusion
The impact of smoking and alcohol on bone health is a significant public health concern that warrants attention. Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to decreased bone density, increased fracture risk, and a higher likelihood of developing osteoporosis. Understanding the mechanisms through which these substances affect bone health is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By adopting healthier lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, and prioritizing nutrition and exercise, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their bone health and overall well-being.