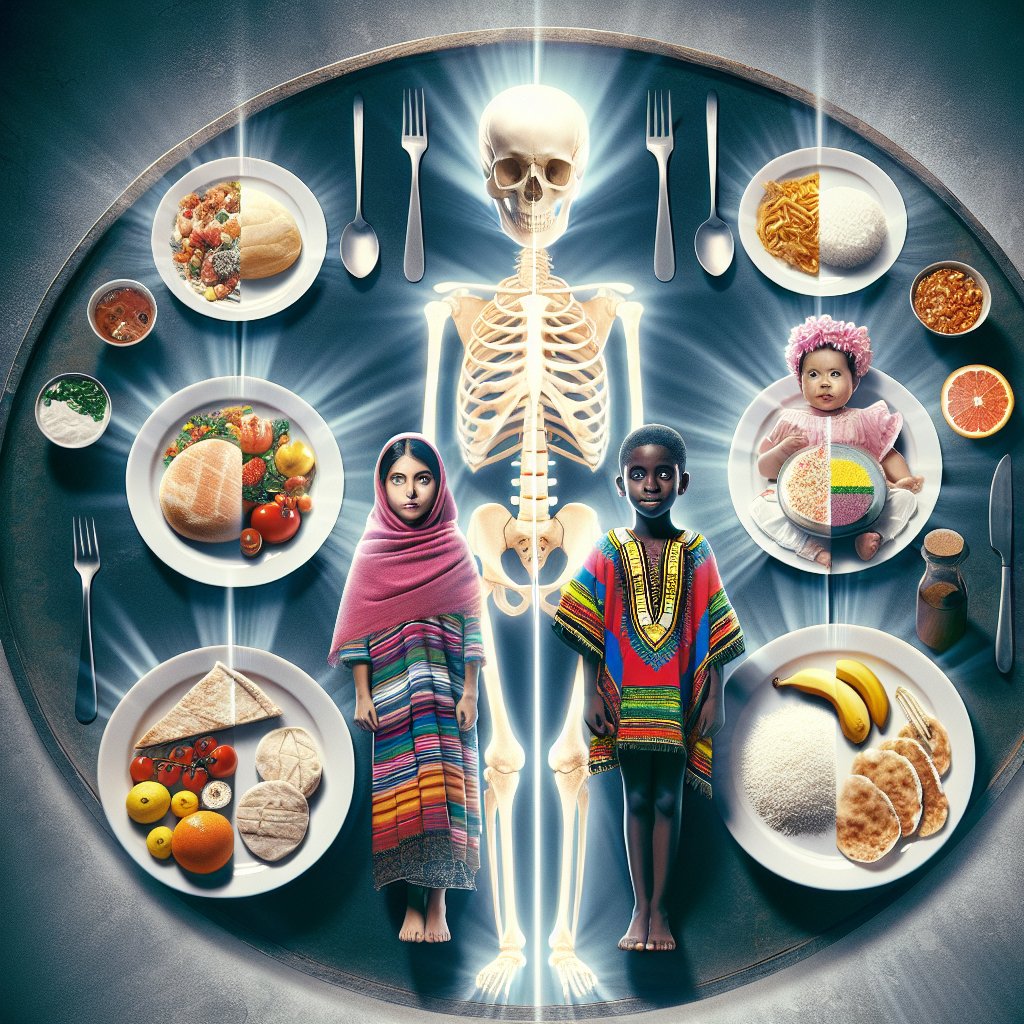
The relationship between cultural diets and bone health is a complex and multifaceted topic that varies significantly across different regions of the world. Understanding how dietary practices influence bone density and overall skeletal health can provide valuable insights into public health strategies and nutritional guidelines. This article explores the various cultural diets and their impact on bone health, examining both traditional practices and modern dietary trends.
Cultural Diets and Their Nutritional Components
Cultural diets are shaped by a variety of factors, including geography, climate, religion, and historical practices. These diets often reflect the local availability of food resources and the traditional methods of food preparation. The nutritional components of these diets play a crucial role in determining their effects on bone health.
Traditional Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil, has been associated with numerous health benefits, including improved bone health. This diet is rich in calcium and vitamin D, both essential for maintaining bone density. Dairy products, particularly yogurt and cheese, are commonly consumed, providing a significant source of calcium.
Moreover, the Mediterranean diet includes fish, which is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, potentially reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Studies have indicated that populations adhering to this diet tend to have higher bone mineral density compared to those following other dietary patterns.
Asian Diets and Bone Health
In many Asian cultures, diets are often plant-based, with a heavy emphasis on rice, vegetables, and legumes. While these diets are generally low in saturated fats and high in fiber, they may lack sufficient calcium and vitamin D, which are critical for bone health. For instance, traditional Chinese diets may include tofu and green leafy vegetables, which provide some calcium, but the overall intake may still fall short of recommended levels.
In contrast, countries like Japan have a unique dietary pattern that includes fish, seaweed, and fermented foods, which can contribute positively to bone health. The consumption of fish provides essential nutrients, including vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for maintaining bone density. Additionally, the Japanese diet often includes soy products, which contain isoflavones that may help in preserving bone mass.
Western Diets and Their Impact
Western diets, particularly those prevalent in the United States and Europe, are often characterized by high consumption of processed foods, red meat, and sugary beverages. These diets tend to be low in fruits and vegetables, which are essential for providing vitamins and minerals necessary for bone health. The high intake of phosphates from processed foods can also lead to an imbalance in calcium levels, negatively affecting bone density.
Furthermore, the increasing trend of lactose intolerance in many Western populations has led to a decrease in dairy consumption, which is a primary source of calcium. This reduction can contribute to lower bone mineral density and a higher risk of fractures, particularly in older adults.
The Role of Lifestyle Factors
While dietary patterns are crucial for bone health, lifestyle factors such as physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption also play significant roles. Engaging in regular weight-bearing exercises can enhance bone strength and density, while sedentary lifestyles can lead to bone loss.
Physical Activity and Bone Health
Physical activity is essential for maintaining healthy bones. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, and resistance training, stimulate bone formation and help prevent bone loss. In cultures where physical activity is integrated into daily life, such as in many Mediterranean and African communities, individuals often exhibit better bone health compared to those in more sedentary societies.
In contrast, modern lifestyles in urban areas often promote sedentary behavior, which can lead to a decline in bone health. The rise of technology and the prevalence of desk jobs have contributed to decreased physical activity levels, particularly among younger generations. This trend is concerning, as it may lead to an increase in osteoporosis and related fractures in the future.
Impact of Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking has been shown to have detrimental effects on bone health, as it can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium and reduce estrogen levels in women, which is crucial for bone maintenance. In cultures where smoking is prevalent, there may be a higher incidence of osteoporosis and fractures.
Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact bone health. While moderate alcohol intake may have some protective effects, heavy drinking is associated with an increased risk of bone loss and fractures. Cultural attitudes towards alcohol consumption can significantly influence bone health outcomes in different populations.
Global Perspectives on Bone Health
Understanding the global perspectives on bone health requires a comprehensive examination of how cultural diets and lifestyle factors interact. Different regions of the world face unique challenges and opportunities in promoting bone health through dietary practices.
Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives aimed at improving bone health often focus on education and awareness regarding the importance of nutrition and physical activity. In many countries, campaigns promoting the consumption of calcium-rich foods and encouraging regular exercise have been implemented to combat the rising rates of osteoporosis.
For instance, in countries with high rates of lactose intolerance, alternative sources of calcium, such as fortified plant-based milks and leafy greens, are promoted. Additionally, community programs that encourage physical activity, particularly among older adults, are essential for maintaining bone health across the lifespan.
Future Directions in Research
Future research on cultural diets and bone health should focus on understanding the specific nutrients that contribute to bone density and how these nutrients interact with lifestyle factors. Longitudinal studies examining the effects of dietary patterns on bone health across different populations will provide valuable insights into effective public health strategies.
Moreover, exploring the role of traditional foods and practices in promoting bone health can help preserve cultural heritage while improving health outcomes. Integrating traditional knowledge with modern nutritional science may lead to innovative approaches to enhance bone health globally.
Conclusion
The impact of cultural diets on bone health is a critical area of study that highlights the importance of nutrition and lifestyle in maintaining skeletal integrity. By understanding the diverse dietary practices around the world and their effects on bone health, we can develop targeted public health initiatives that promote healthier lifestyles and improve bone health outcomes for individuals across different cultures.
As we continue to explore the intricate relationship between diet, lifestyle, and bone health, it is essential to recognize the value of cultural diversity in shaping our understanding of nutrition and health. Embracing this diversity can lead to more effective strategies for preventing osteoporosis and promoting overall well-being worldwide.