Bone infections, also known as osteomyelitis, are serious medical conditions that can lead to significant health complications if not treated promptly. These infections can affect any bone in the body and are often caused by bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of bone infections is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This article will delve into the various aspects of bone infections, providing a comprehensive overview for better awareness and understanding.
Causes of Bone Infections
Bone infections can arise from a variety of sources, and identifying the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment. The most common causes include:
- Direct Inoculation: This occurs when bacteria or other pathogens enter the bone through an open fracture, surgical procedure, or penetrating injury. For instance, if a person sustains a deep cut that exposes the bone, the risk of infection increases significantly.
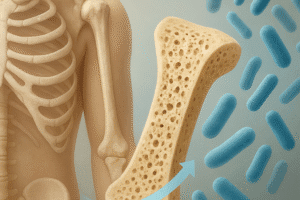
- Hematogenous Spread: In some cases, infections can spread to the bones from other parts of the body through the bloodstream. Conditions such as skin infections, dental infections, or infections in other organs can lead to osteomyelitis if the pathogens travel through the circulatory system.
- Contiguous Spread: This type of infection occurs when an adjacent infected tissue spreads to the bone. For example, a severe skin infection or an abscess can extend into the underlying bone, leading to osteomyelitis.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and immunocompromised states, can increase the risk of developing bone infections. These conditions can impair the body’s ability to fight infections and promote the growth of pathogens.
Symptoms of Bone Infections
The symptoms of bone infections can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the specific bone affected. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain: One of the most prominent symptoms of a bone infection is localized pain in the affected area. The pain may be constant or may worsen with movement or pressure.
- Swelling and Redness: The area around the infected bone may become swollen, red, and warm to the touch. This inflammation is a response to the infection and can be accompanied by tenderness.
- Fever and Chills: Systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, and fatigue may occur as the body attempts to fight off the infection. These symptoms can indicate a more severe or widespread infection.
- Limited Range of Motion: Infections in bones that are part of a joint can lead to stiffness and a reduced range of motion. This can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
- Drainage: In some cases, an abscess may form, leading to the drainage of pus or other fluids from the infected area. This can be a clear sign of a bone infection that requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of Bone Infections
Diagnosing a bone infection typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may use the following methods to confirm the presence of osteomyelitis:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential for identifying symptoms and risk factors associated with bone infections. The healthcare provider will assess the affected area for signs of infection and inquire about any recent injuries or underlying health conditions.
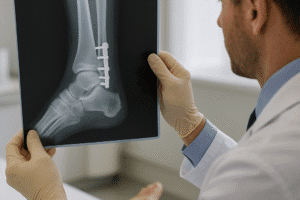
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans can help visualize the affected bone and surrounding tissues. These imaging techniques can reveal changes in bone structure, the presence of abscesses, or other abnormalities indicative of infection.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for elevated white blood cell counts or inflammatory markers, which can suggest an infection. Additionally, cultures of any drainage or tissue samples may be taken to identify the specific pathogen responsible for the infection.
Treatment Options for Bone Infections
Treating bone infections requires a multifaceted approach that may include antibiotics, surgery, and supportive care. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection, the underlying cause, and the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
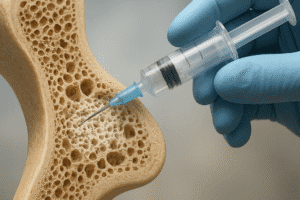
- Antibiotic Therapy: The cornerstone of treatment for bone infections is antibiotic therapy. Depending on the type of bacteria or pathogen identified, healthcare providers will prescribe appropriate antibiotics, which may be administered orally or intravenously. In some cases, long-term antibiotic therapy may be necessary to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases or when there is the presence of abscesses or necrotic tissue, surgical intervention may be required. This can involve draining abscesses, removing infected tissue, or even performing a bone graft to promote healing.
- Supportive Care: Patients may benefit from supportive care measures, such as pain management, physical therapy, and nutritional support. These interventions can help improve overall recovery and quality of life.
Prevention of Bone Infections
Preventing bone infections is crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk due to underlying health conditions or previous injuries. Some preventive measures include:
- Proper Wound Care: Prompt and appropriate care of wounds, especially deep cuts or fractures, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Keeping wounds clean and covered is essential.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Individuals with chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their conditions effectively. This includes regular check-ups and monitoring for any signs of infection.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date with vaccinations can help prevent infections that may lead to osteomyelitis. Vaccines for conditions such as influenza and pneumonia can be particularly beneficial.
Conclusion
Bone infections are serious medical conditions that require prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. By being aware of the risk factors and taking appropriate preventive measures, individuals can reduce their chances of developing osteomyelitis and ensure better health outcomes. If you suspect a bone infection, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly to avoid complications and promote recovery.