The role of zinc in promoting bone health is a topic of increasing interest among researchers and health professionals alike. Zinc, an essential trace mineral, plays a crucial role in various biological functions, including immune response, protein synthesis, and cell division. However, its significance in maintaining and enhancing bone health is often overlooked. This article delves into the multifaceted role of zinc in bone metabolism, its mechanisms of action, and the implications of zinc deficiency on skeletal health.
Zinc and Bone Metabolism
Bone metabolism is a complex process involving the continuous remodeling of bone tissue, which is essential for maintaining bone strength and integrity. This process is regulated by a balance between bone formation and bone resorption, with osteoblasts and osteoclasts playing pivotal roles, respectively. Zinc is known to influence both of these cell types, thereby impacting overall bone health.
The Role of Zinc in Osteoblast Function
Osteoblasts are the cells responsible for bone formation. They synthesize and secrete the bone matrix, which is primarily composed of collagen and other proteins. Zinc is vital for osteoblast function due to its involvement in several key processes:
- Collagen Synthesis: Zinc is a cofactor for enzymes involved in collagen synthesis, which is crucial for the structural integrity of bone.
- Gene Expression: Zinc influences the expression of genes related to osteoblast differentiation and activity, promoting the formation of new bone tissue.
- Mineralization: Zinc plays a role in the mineralization process, where calcium and phosphate are deposited in the bone matrix, contributing to bone density.
Research has shown that adequate zinc levels are associated with increased osteoblast activity and enhanced bone formation. Conversely, zinc deficiency can lead to impaired osteoblast function, resulting in decreased bone formation and increased risk of fractures.
The Role of Zinc in Osteoclast Function
Osteoclasts are responsible for bone resorption, a process that removes old or damaged bone tissue. While this process is essential for bone remodeling, excessive osteoclast activity can lead to bone loss. Zinc also plays a role in regulating osteoclast function:
- Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis: Zinc has been shown to inhibit the differentiation of precursor cells into osteoclasts, thereby reducing bone resorption.
- Regulation of Cytokines: Zinc modulates the production of cytokines that are involved in osteoclast activation, helping to maintain a balance between bone formation and resorption.
By influencing both osteoblast and osteoclast activity, zinc helps maintain the delicate balance necessary for healthy bone metabolism. This dual role underscores the importance of adequate zinc intake for optimal bone health.
Zinc Deficiency and Its Impact on Bone Health
Zinc deficiency is a global health concern, particularly in developing countries where dietary intake may be insufficient. The consequences of zinc deficiency extend beyond immune dysfunction and growth retardation; it can significantly impact bone health as well.
Consequences of Zinc Deficiency
Several studies have demonstrated the adverse effects of zinc deficiency on bone health:
- Decreased Bone Density: Zinc deficiency has been linked to lower bone mineral density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Impaired Bone Healing: Individuals with zinc deficiency may experience delayed bone healing following fractures or surgical interventions.
- Increased Risk of Osteoporosis: Long-term zinc deficiency can contribute to the development of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women who are already at higher risk due to hormonal changes.
Furthermore, zinc deficiency can exacerbate the effects of other nutritional deficiencies, such as calcium and vitamin D, further compromising bone health. This highlights the importance of a well-balanced diet that includes adequate levels of zinc to support skeletal integrity.
Sources of Zinc
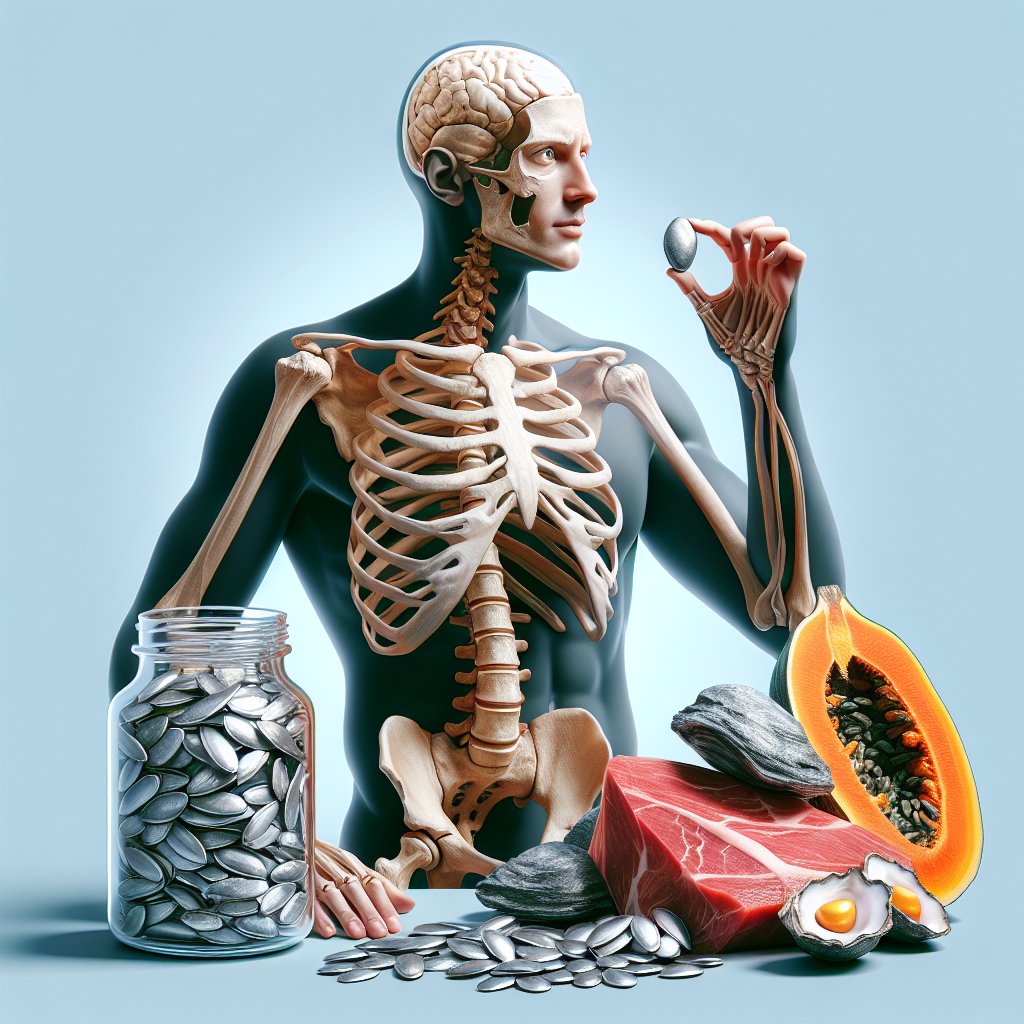
To prevent zinc deficiency and promote bone health, it is essential to include zinc-rich foods in the diet. Some excellent sources of zinc include:
- Meat: Red meat, poultry, and seafood are among the richest sources of zinc.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt provide a good amount of zinc along with other essential nutrients.
- Nuts and Seeds: Pumpkin seeds, cashews, and almonds are plant-based sources of zinc.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas contain zinc, although it is less bioavailable than that from animal sources.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like oats and quinoa also contribute to zinc intake.
For individuals who may struggle to meet their zinc needs through diet alone, supplementation may be considered. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, as excessive zinc intake can lead to toxicity and adverse health effects.
Conclusion
The role of zinc in promoting bone health is multifaceted and significant. As an essential trace mineral, zinc supports osteoblast and osteoclast function, contributing to the delicate balance of bone remodeling. Zinc deficiency can have detrimental effects on bone density, healing, and overall skeletal health, underscoring the importance of adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation. By prioritizing zinc-rich foods and maintaining optimal zinc levels, individuals can support their bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures as they age.