The process of bone fusion in spine surgery is a critical aspect of treating various spinal disorders and injuries. This surgical technique aims to stabilize the spine by promoting the growth of new bone between two or more vertebrae, effectively fusing them together. Understanding the intricacies of this process is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals, as it can significantly impact recovery outcomes and overall spinal health.
Understanding Bone Fusion
Bone fusion, also known as spinal fusion, is a surgical procedure designed to eliminate motion between vertebrae. This is particularly important in cases where the spine is unstable due to conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, or spinal fractures. The primary goal of spinal fusion is to relieve pain, restore stability, and improve the patient’s quality of life.
The Biological Mechanism of Bone Fusion
The process of bone fusion relies on the body’s natural healing mechanisms. When a bone is fractured or surgically altered, the body initiates a healing response that involves several stages:
- Inflammation: This initial phase occurs immediately after the injury or surgery. Blood vessels in the area are damaged, leading to bleeding and the formation of a hematoma. Inflammatory cells migrate to the site, releasing cytokines that promote healing.
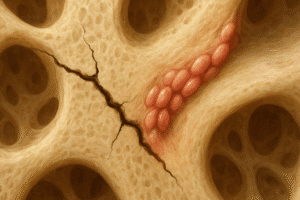
- Soft Callus Formation: Within a few days, a soft callus made of collagen and cartilage begins to form around the fracture site. This provides a temporary scaffold for new bone growth.
- Hard Callus Formation: Over the next few weeks, the soft callus is gradually replaced by a hard callus made of woven bone. This process is known as ossification and is crucial for stabilizing the spine.
- Bone Remodeling: Finally, the hard callus is remodeled into mature bone over several months. This phase ensures that the bone regains its strength and structural integrity.
In spinal fusion surgery, surgeons often use bone grafts to facilitate this process. Bone grafts can be harvested from the patient (autograft), obtained from a donor (allograft), or created synthetically (synthetic grafts). The choice of graft material can influence the success of the fusion.
Types of Spinal Fusion Techniques
There are several techniques used in spinal fusion surgery, each tailored to the specific needs of the patient:
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF): This technique involves accessing the spine from the back and removing the intervertebral disc. A bone graft is then placed in the disc space to promote fusion.
- Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF): In this approach, the surgeon accesses the spine from the front. This method allows for direct visualization of the disc space and can lead to less muscle disruption.
- Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF): Similar to PLIF, this technique involves accessing the spine from the side, allowing for a less invasive approach while still achieving effective fusion.
- Minimally Invasive Spinal Fusion: Advances in technology have led to the development of minimally invasive techniques that reduce tissue damage and promote faster recovery.
Factors Influencing Bone Fusion Success
While spinal fusion can be highly effective, several factors can influence the success of the procedure. Understanding these factors is crucial for both patients and surgeons.
Patient-Related Factors
Several patient-related factors can impact the healing process:
- Age: Older patients may experience slower healing due to decreased bone density and slower metabolic rates.
- Smoking: Tobacco use has been shown to impair bone healing and increase the risk of fusion failure.
- Comorbidities: Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and osteoporosis can negatively affect the body’s ability to heal.
- Activity Level: Patients who engage in regular physical activity may experience better outcomes compared to sedentary individuals.
Surgical Factors
The surgical technique and the surgeon’s experience also play a significant role in the success of spinal fusion:
- Technique Used: The choice of surgical technique can influence the amount of disruption to surrounding tissues and the effectiveness of the fusion.
- Surgeon Experience: A skilled surgeon with experience in spinal fusion is more likely to achieve successful outcomes.
- Postoperative Care: Proper postoperative care, including physical therapy and adherence to activity restrictions, is essential for promoting healing.
Postoperative Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from spinal fusion surgery is a gradual process that requires patience and commitment. Understanding what to expect during the recovery phase can help patients prepare for their journey toward healing.
Immediate Postoperative Care
Following surgery, patients are typically monitored in a recovery room for several hours. Pain management is a priority during this time, and medications may be administered to control discomfort. Patients are usually encouraged to begin moving as soon as possible to promote circulation and prevent complications.
Rehabilitation Process
The rehabilitation process is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes after spinal fusion. It typically involves:
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist will design a personalized rehabilitation program that includes exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Activity Modification: Patients are advised to avoid high-impact activities and heavy lifting during the initial recovery phase to protect the surgical site.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process and address any concerns.
Conclusion
The process of bone fusion in spine surgery is a complex yet vital procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from spinal disorders. By understanding the biological mechanisms, surgical techniques, and factors influencing success, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options. With proper care and rehabilitation, many patients can achieve successful outcomes and return to their daily activities with reduced pain and increased stability.