Understanding the healing timeline for common bone fractures is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. Bone fractures are a prevalent injury that can occur due to various reasons, including accidents, falls, or sports injuries. The healing process can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of fracture, the age and health of the individual, and the treatment method employed. This article will explore the different types of bone fractures, the stages of healing, and the factors that influence recovery time.
Types of Bone Fractures
Bone fractures can be classified into several categories based on their characteristics and the mechanism of injury. Understanding these types is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and estimating the healing timeline.
1. Closed vs. Open Fractures
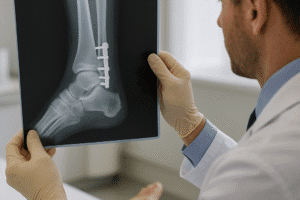
Fractures can be categorized as closed or open. A closed fracture occurs when the bone breaks but does not pierce the skin, while an open fracture, also known as a compound fracture, involves a break that results in the bone protruding through the skin. Open fractures are generally more serious due to the risk of infection and may require more extensive treatment.
2. Complete vs. Incomplete Fractures
Complete fractures involve a break that goes all the way through the bone, resulting in two separate pieces. Incomplete fractures, on the other hand, do not fully separate the bone and may include hairline fractures or greenstick fractures, which are more common in children due to their flexible bones.
3. Specific Types of Fractures
- Transverse Fracture: A straight break across the bone.
- Oblique Fracture: A diagonal break across the bone.
- Spiral Fracture: A fracture that twists around the bone, often caused by a rotational force.
- Comminuted Fracture: The bone is shattered into several pieces, often due to high-impact trauma.
- Stress Fracture: A small crack in the bone caused by repetitive force or overuse, common in athletes.
The Healing Process
The healing process for bone fractures typically occurs in several stages, each playing a vital role in restoring the bone’s integrity and function. Understanding these stages can help patients manage their expectations and adhere to treatment plans.
1. Inflammatory Phase
The healing process begins immediately after the fracture occurs. In this inflammatory phase, the body responds to the injury by sending blood to the area, which helps to form a clot around the fracture site. This clot serves as a temporary scaffold for new tissue and is crucial for the healing process. Inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and bruising, which are common symptoms following a fracture.
2. Reparative Phase
After a few days, the reparative phase begins. During this stage, the body starts to form a soft callus made of collagen and cartilage around the fracture site. This soft callus gradually transforms into a hard callus as new bone cells, known as osteoblasts, begin to produce new bone material. This phase can last several weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture and the individual’s overall health.
3. Remodeling Phase
The final stage of healing is the remodeling phase, which can last for months or even years. During this time, the hard callus is gradually replaced with mature bone tissue. The bone is reshaped and strengthened through a process called bone remodeling, where old bone is removed by cells called osteoclasts, and new bone is formed. This phase is crucial for restoring the bone’s original strength and function.
Factors Influencing Healing Time
Several factors can influence the healing time for bone fractures. Understanding these factors can help patients and healthcare providers set realistic expectations for recovery.
1. Age
Age plays a significant role in the healing process. Children and adolescents typically heal faster than adults due to their higher metabolic rates and the presence of growth factors. In contrast, older adults may experience slower healing times due to decreased bone density and slower cellular processes.
2. Type of Fracture
The type and severity of the fracture also impact healing time. Simple fractures may heal within a few weeks, while complex fractures, such as comminuted fractures, may take several months to heal fully. Additionally, fractures that involve joints or are associated with significant soft tissue damage may require longer recovery times.
3. Overall Health
A person’s overall health and medical history can significantly affect healing. Conditions such as diabetes, osteoporosis, and smoking can impede the healing process. Patients with compromised immune systems or those taking certain medications may also experience delayed healing.
4. Treatment Method
The method of treatment chosen for the fracture can influence recovery time. Non-surgical treatments, such as casting or splinting, may allow for quicker healing in some cases, while surgical interventions, such as internal fixation or external fixation, may be necessary for more complex fractures. The choice of treatment should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering the specific circumstances of the injury.
Conclusion
Understanding the healing timeline for common bone fractures is essential for effective recovery. By recognizing the types of fractures, the stages of healing, and the factors that influence recovery time, patients can better navigate their healing journey. It is crucial to follow medical advice, engage in appropriate rehabilitation exercises, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support the healing process. With patience and proper care, most individuals can expect to return to their normal activities following a fracture.